Blockchain technology is a revolutionary concept that underlies cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers in a secure and transparent manner. Instead of relying on a central authority, blockchain relies on consensus algorithms to validate and record transactions, ensuring immutability and reducing the risk of fraud or tampering. This technology has the power to transform various industries by enabling secure and verifiable data sharing, smart contracts, and enhanced supply chain transparency, fostering a new level of trust and efficiency in digital interactions.
History of Blockchain
Ever wondered what powered the financial revolution in the tech-savvy world? Blockchain! It’s not just a buzzword; it’s a groundbreaking technology. Tracing back to 2008, the mysterious figure, Satoshi Nakamoto, first introduced blockchain as the underlying structure for Bitcoin. This digital ledger technology was conceptualized to offer transparency, security, and decentralization, marking a departure from traditional centralized systems.
Core Components of Blockchain
A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks containing digital information. It comprises three primary components:
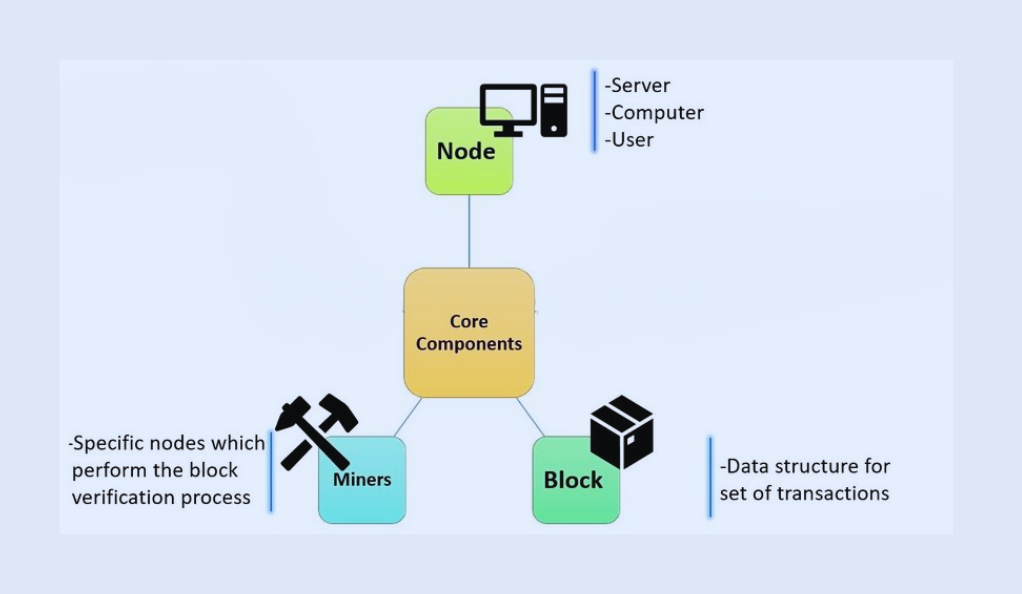
- Blocks: These are digital storage units that contain data, nonce, and the hash of the previous block. Every block is a chronological representation of data, ensuring integrity and traceability.
- Nodes: Nodes are individual computers that enforce consensus across the network. They maintain and validate the blockchain, making sure every transaction adheres to the network’s protocol.
- Miners: Miners are special nodes that validate and add transactions to the block. Through computational processes, miners solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the chain, securing the network further.
Understanding Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin – The Pioneer
Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, is like digital gold in the fintech world. Created in 2009, it opened a new era of decentralized finance, free from governmental control. This decentralized digital currency allows for peer-to-peer transactions without an intermediary. Bitcoin’s unique value proposition lies in its finite supply, decentralized nature, and potential to act as a hedge against inflation.
Altcoins and Their Impact
Following Bitcoin, a plethora of alternative cryptocurrencies (Altcoins) sprang up. From Ethereum to Ripple, these altcoins are reshaping the financial landscape with unique features and use cases. While Bitcoin remains the dominant player, altcoins have found niches, with some focusing on faster transaction speeds, privacy, or entirely different use cases, like decentralized applications or tokenized assets. The diverse ecosystem ensures that there’s a cryptocurrency for every need.
Smart Contracts: Changing the Landscape
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts are digital agreements that execute themselves. Imagine them as vending machines: you put something in, and the contract does the rest! Running on blockchain, they automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. These contracts are tamper-proof and transparent. Unlike traditional contracts, they’re not subject to interpretation, ensuring all parties adhere to the agreed terms.
Use Cases and Benefits
From buying property to securing copyrights, smart contracts offer a transparent and automated way of executing agreements. Industries worldwide are experiencing transformations through these contracts, simplifying processes and reducing fraud. The real estate industry, for instance, can benefit from instantaneous title transfers. Meanwhile, the entertainment industry can ensure artists are paid promptly through automated royalty distribution systems.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
What are DApps?
DApps, or decentralized applications, are programs run by many users on a decentralized network. Imagine them like your regular apps, but without a central server. This ensures they’re resistant to censorship and are often more secure than traditional applications. DApps have the potential to redefine online platforms, giving users more control and autonomy.
Real-World Examples
From gaming platforms to decentralized exchanges, DApps have been making inroads in various domains. One example is decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which offer financial services without traditional intermediaries. Another is decentralized marketplaces, allowing users to trade goods and services with minimal fees and without centralized control. The innovation in this space is accelerating, signaling a shift towards more decentralized online platforms.
Future of Blockchain Technology
Trends and Predictions
The realm of blockchain is not confined to cryptocurrencies; it’s an ever-expanding field. From healthcare to logistics, the potential applications are seemingly endless. As industries begin to recognize the benefits, the adoption rate of blockchain-based solutions will likely surge. Soon, it might become commonplace to see supply chains tracked on blockchain or medical records securely stored on decentralized platforms.
Opportunities and Challenges
Blockchain presents numerous opportunities, from revolutionizing industries to providing transparency in public sectors. However, challenges such as scalability, energy consumption, and interoperability need addressing. As with any nascent technology, it’s a balancing act between potential and pitfalls. Yet, with continuous advancements, many believe these challenges will soon be a thing of the past, paving the way for a decentralized future.
Conclusion
Blockchain is much more than just the technology behind cryptocurrencies. It’s a paradigm shift, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the digital realm. With its promise of decentralization, transparency, and security, blockchain stands as a beacon of hope for a more equitable digital future. So, as we move forward, the question isn’t whether blockchain will influence our lives, but how profoundly it will.
FAQs
Blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring security and transparency.
Cryptocurrencies work on blockchain technology, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority.
Smart contracts are automated digital contracts that execute themselves when predefined conditions are met.
DApps run on a decentralized network, removing the need for a central server, offering enhanced security and control.
The future of blockchain technology is promising, with wide-ranging applications across various industries, including healthcare, logistics, and finance.
Bitcoinnewsmagazine is committed to providing impartial and reliable insights into cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. It's important to note that we do not provide financial advice, and we strongly encourage users to conduct their own research and due diligence.
Read More
