Introduction: Beyond Bitcoin’s Shadow
The rise of Bitcoin introduced the world to blockchain technology, but its potential has far-reaching implications. Beyond the scope of digital currency, blockchain holds the promise of transforming various industries by enabling secure, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping.

Blockchain technology’s inherent security and transparency make it an ideal candidate for various use cases beyond cryptocurrencies. For instance, in the realm of supply chain management, blockchain can track the journey of products from raw materials to the end consumer, ensuring authenticity, reducing fraud, and improving accountability. Similarly, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry by securely storing patient data and enabling interoperability between different healthcare providers, ultimately leading to more efficient and patient-centric care.
Smart Contracts: The Backbone of Automation
Smart contracts, the digital equivalent of traditional contracts, are coded agreements that automatically execute predefined actions when certain conditions are met. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and enhancing efficiency across a multitude of processes.
In the world of blockchain, smart contracts operate autonomously and securely. When certain criteria are fulfilled, the contract’s terms are automatically executed without requiring third-party intervention. This technology finds applications in areas such as supply chain management, real estate transactions, and even self-executing insurance policies. The immutability of blockchain ensures that once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered, adding an extra layer of security and trust to these automated agreements.
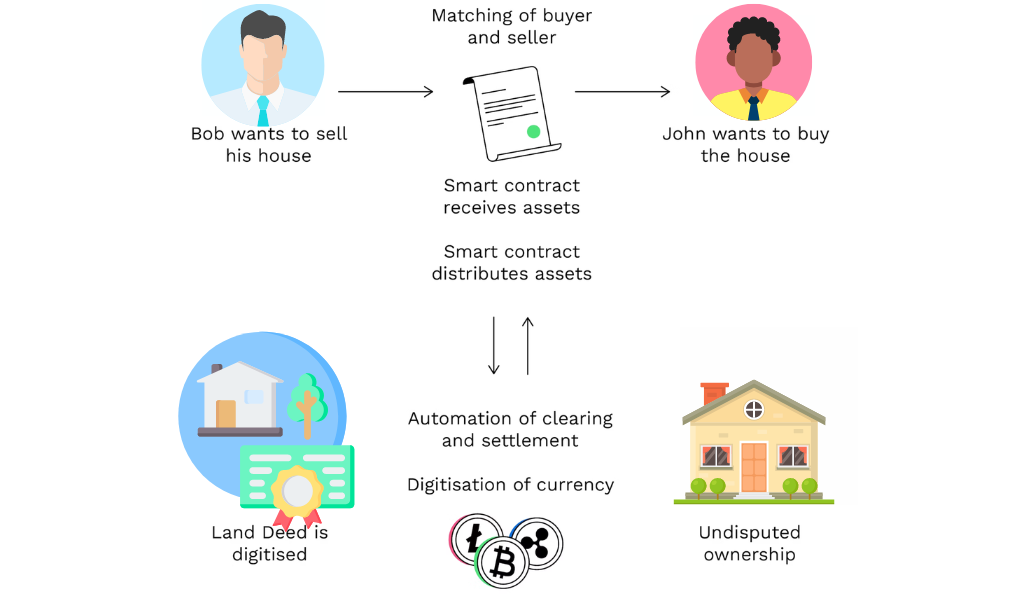
Smart contracts have the potential to disrupt traditional industries by streamlining complex workflows and reducing the need for intermediaries. For instance, in real estate, smart contracts can automate the transfer of property ownership once certain conditions, such as payment and legal approvals, are met. This not only speeds up the process but also minimizes the risk of fraud. In the entertainment industry, artists can use smart contracts to automate royalty payments for their digital creations, ensuring that they receive fair compensation without relying on intermediaries.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Reshaping Traditional Banking
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a rapidly growing sector within the blockchain ecosystem that aims to reconstruct traditional financial systems using decentralized technologies. Unlike traditional banks that act as intermediaries, DeFi platforms operate on blockchain networks, enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for centralized control.
One of the key innovations of DeFi is the concept of “yield farming,” where individuals can lend out their cryptocurrencies and earn interest in return. Additionally, users can trade a wide array of digital assets directly on DeFi platforms, reducing the need for traditional exchanges. The ability to bypass intermediaries and access financial services directly has the potential to make financial services more accessible and inclusive, especially for individuals in underserved regions.
The DeFi ecosystem offers a range of financial products and services, including decentralized lending and borrowing, stablecoins, and decentralized exchanges. These platforms are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, enabling individuals from around the world to participate in the global financial system without relying on traditional banks. However, the rapid growth of DeFi has also raised concerns about security and regulatory challenges, highlighting the need for robust governance mechanisms and risk management strategies.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Transforming Digital Ownership
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have revolutionized how we perceive ownership in the digital age. While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are fungible, meaning one unit is interchangeable with another, NFTs represent unique digital assets that cannot be replicated or replaced. This uniqueness has given rise to an entirely new market for digital art, collectibles, virtual real estate, and more.
NFTs are changing the game for creators, allowing them to tokenize their digital creations and sell them as provably scarce assets on blockchain platforms. Artists, musicians, and even content creators are finding new revenue streams through NFT sales. Collectors, on the other hand, are eager to own these unique digital items, and the scarcity and provenance provided by blockchain technology add significant value to NFTs.
The use cases for NFTs extend beyond the art world. For example, in the gaming industry, NFTs can represent in-game items, characters, and land ownership, enabling players to truly own and trade their virtual assets. In real estate, NFTs can represent ownership of physical properties, allowing for fractional ownership and easier transfer of property rights. While NFTs have unlocked exciting opportunities, the market is also grappling with issues of copyright, environmental impact, and speculative bubbles, highlighting the need for responsible adoption and regulation.
Interoperability: Bridging the Blockchain Gap
One of the challenges in the blockchain space is the lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks. Each blockchain often operates in isolation, hindering the seamless flow of data and value between them. Interoperability solutions aim to bridge this gap by enabling different blockchains to communicate and share information.
Interoperability is essential for the mass adoption of blockchain technology. Without the ability to seamlessly interact with other networks, blockchain applications can become isolated silos, limiting their potential impact. Various projects are working on interoperability protocols and frameworks that allow different blockchains to exchange data and assets securely and efficiently.
Cross-chain interoperability can have far-reaching implications. It can enable the transfer of assets between different blockchains, making it easier to trade cryptocurrencies and other digital assets across networks. Additionally, interoperability can facilitate the development of decentralized applications (DApps) that span multiple blockchains, enabling complex functionalities that leverage the strengths of different networks.
Scalability Solutions: Overcoming Network Constraints
Scalability has been a persistent challenge for blockchain networks. As more users join a blockchain network, the transaction processing capacity needs to scale accordingly. However, traditional blockchain architectures, like the one used by Bitcoin, have limitations on the number of transactions they can handle per second.
Privacy and Security Enhancements: Guarding Against Threats
While blockchain is celebrated for its transparency and immutability, privacy remains a critical concern, especially for enterprise adoption. Public blockchains expose transaction details to all participants, which is not always desirable for business use cases.
To address these concerns, various privacy-focused solutions have emerged. Zero-knowledge proofs, for example, allow participants to prove the validity of a transaction without revealing the underlying data. This technology ensures that sensitive information remains private while still allowing for secure and verifiable transactions.
Security enhancements are also crucial to protect blockchain networks from cyber threats. Decentralized networks are not immune to attacks, and developers continuously work on improving the security of blockchain protocols. Advanced cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and regular audits play a vital role in safeguarding blockchain networks from malicious actors.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Energy-Efficient Validation
Blockchain networks rely on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network. One of the most well-known consensus mechanisms is Proof of Work (PoW), which requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks to the blockchain.
Proof of Work, while effective, has come under scrutiny due to its energy-intensive nature. Miners compete to solve puzzles, consuming significant amounts of electricity in the process. This energy consumption has led to concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain networks using PoW.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus mechanism that addresses these environmental concerns. In a PoS system, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining and significantly reduces the carbon footprint of blockchain networks.
PoS not only offers environmental benefits but also enhances network security. Validators have a financial stake in the network’s integrity, as they can lose their staked tokens if they act maliciously. This economic incentive aligns the interests of validators with the network’s well-being, resulting in a more secure and energy-efficient consensus mechanism.
Governance Models: Democratizing Decision-Making
Blockchain’s decentralized nature extends beyond technology; it also affects decision-making processes within the network. Traditional centralized systems are governed by a single entity or a group of individuals. In contrast, blockchain networks often employ decentralized governance models that allow participants to collectively make decisions about the network’s future.

Decentralized governance is typically achieved through on-chain voting mechanisms. Token holders can participate in important decisions, such as protocol upgrades, changes to network parameters, and the allocation of resources. This democratic approach ensures that the interests of the community are taken into account and reduces the concentration of power.
Decentralized governance models empower participants to actively contribute to the network’s development and evolution. It fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members, driving innovation and ensuring that blockchain networks remain adaptable and responsive to changing needs.
Real-World Applications: Industries Riding the Blockchain Wave
Blockchain technology has found applications beyond the realm of digital currency, and various industries are now leveraging its capabilities to solve complex problems. Here are a few notable examples of industries embracing blockchain technology:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it ideal for tracking and verifying the origins and journey of products throughout the supply chain. Each step of the supply chain can be recorded on the blockchain, providing an auditable and tamper-proof record of every transaction.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, blockchain can facilitate secure sharing of patient data across different healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy. Patients can have more control over their medical records and grant access to specific healthcare professionals as needed.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can provide a tamper-resistant and transparent voting system, potentially increasing voter trust and reducing fraud. Each vote is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring its immutability and enabling voters to verify their choices.
- Real Estate: Blockchain’s ability to create tamper-proof records can streamline property transactions, reducing paperwork and the risk of fraud. Property ownership records can be securely stored on the blockchain, simplifying the transfer of ownership and making the process more efficient.
- Gaming: Blockchain is revolutionizing the gaming industry by enabling true ownership of in-game assets. Gamers can buy, sell, and trade digital items using NFTs, allowing them to retain value and ownership even when switching games or platforms.
These examples illustrate how blockchain technology is disrupting traditional processes and providing innovative solutions across various sectors. The transparency, security, and efficiency offered by blockchain have the potential to reshape industries and improve the lives of individuals around the world.
Environmental Concerns: Addressing the Energy Debate
As blockchain adoption grows, so do concerns about its environmental impact, particularly in the case of energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms. The energy consumption required for PoW mining has raised questions about the sustainability of blockchain networks.
The environmental concerns associated with PoW have led to the exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS). PoS offers a more energy-efficient approach to validating transactions and securing the blockchain. Validators, also known as “stakers,” are chosen to create new blocks and verify transactions based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to lock up as collateral.
By transitioning to PoS or other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, blockchain networks can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. This transition aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promotes the sustainable growth of the blockchain industry.
Future Prospects: Evolution and Adaptation
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, and its evolution holds great promise. As scalability, privacy, and interoperability solutions continue to develop, blockchain will likely see broader adoption across various sectors, revolutionizing how industries operate.
Scalability solutions, such as sharding and layer-2 protocols, aim to increase the transaction throughput of blockchain networks, making them more suitable for mainstream applications. These solutions can enable faster and cheaper transactions, making blockchain technology more accessible to a wider audience.
Privacy-enhancing technologies will also play a crucial role in the evolution of blockchain. By providing robust privacy solutions, blockchain networks can cater to a broader range of use cases, including those that require data confidentiality and compliance with regulations like GDPR.
Interoperability efforts will bridge the gap between different blockchains, enabling seamless communication and value transfer across networks. This will facilitate the creation of decentralized applications that leverage the strengths of multiple blockchains, unlocking new levels of innovation and functionality.
Conclusion: Unleashing Blockchain’s Full Potential
The journey of blockchain from its association with Bitcoin to becoming a technology shaping industries exemplifies its transformative power. The innovative applications, decentralization, and potential to disrupt traditional systems pave the way for a promising future.
Blockchain technology’s impact extends beyond financial transactions, revolutionizing supply chains, healthcare, voting systems, real estate, and various other sectors. As the technology continues to evolve and address its challenges, it will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of how we interact, transact, and innovate.
FAQs
Blockchain technology serves as a decentralized and transparent ledger system with applications extending beyond financial transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with terms directly written in code, automating and verifying contract execution.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) revolutionize digital ownership by representing unique items or artworks on the blockchain.
DeFi platforms leverage blockchain to recreate financial services, providing individuals with greater control over their assets and transactions.
Scalability and energy consumption are two key challenges in blockchain adoption, with ongoing efforts to develop efficient solutions.
Bitcoinnewsmagazine is committed to providing impartial and reliable insights into cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. It's important to note that we do not provide financial advice, and we strongly encourage users to conduct their own research and due diligence.
Read More
